Part 1: Pole Height: Single-view metrology corresponds to a set of techniques for making 3D measurements from a single 2D image. Such measurements have several applications including, for example, measuring the height of a suspect in a crime-scene photo. We will consider a simple scenario of single-view metrology to make some 3D measurements from an image.
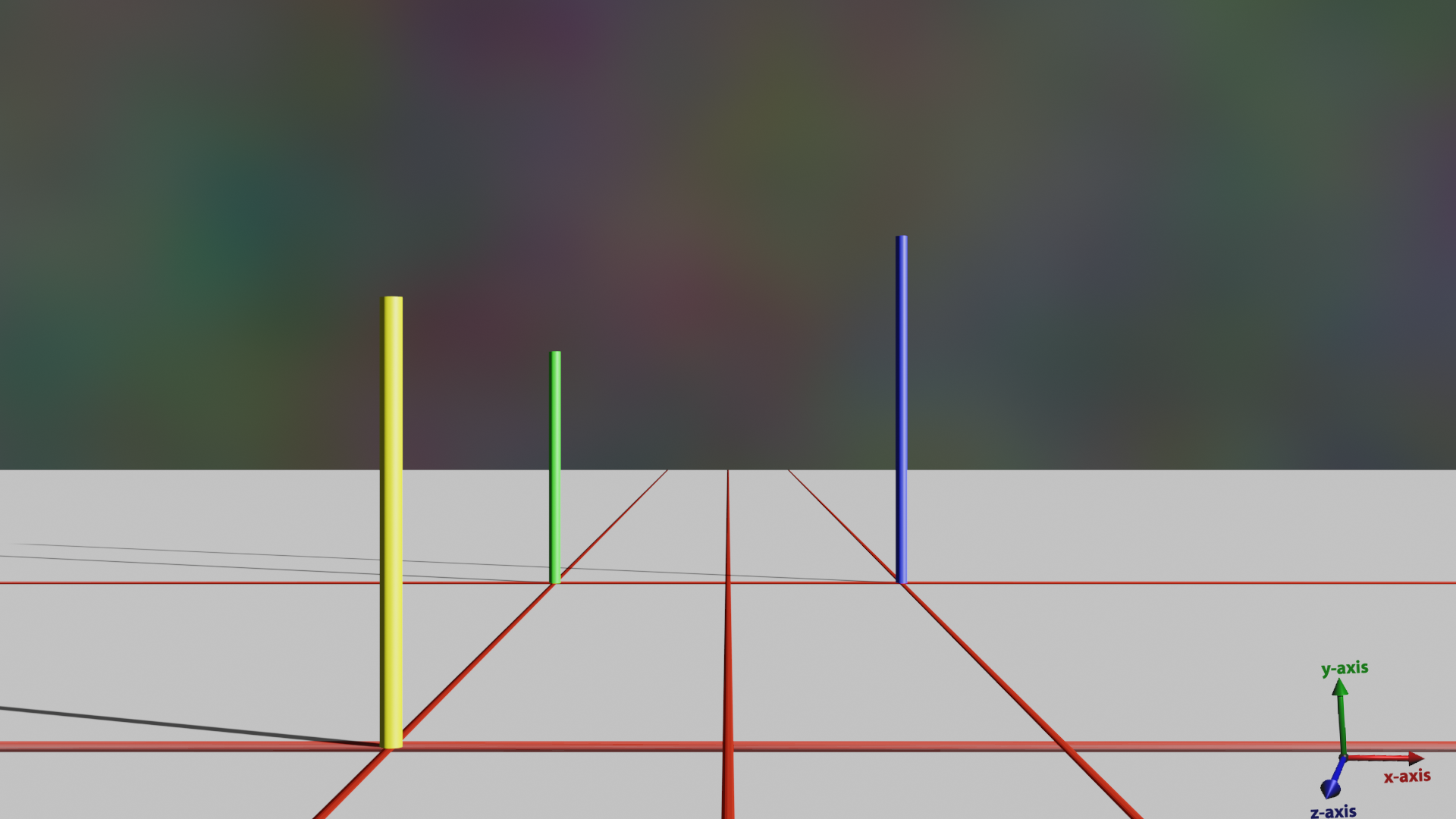
Consider the image below. You are given the following information about the 3D scene. There are three poles colored yellow, green, and blue, and a ground plane in this scene. The three poles are perpendicular to the ground plane. The ground plane is parallel to the X-Z plane, and the camera's optical axis is parallel to the Z-axis. Standing at 4 meters, the yellow and green poles are of the same height in the 3D scene. The distance between these two poles is 17 meters. The green and blue poles are at the same, but unknown, distance from the camera. Finally, the image sensor of the camera has 53,333 pixels per meter.
Recall the perspective projection equation that tells us the relationship between a point's location in the 3D world (X,Y,Z), the camera focal length (f), and the projection of that point in the image (x,y): x=fX/Z, y=fY/Z. Using the above perspective projection equations, compute:
- 1. the camera focal length (f), in mm
- 2. the 3D height (Y) of the blue pole, in m
Write a python script to measure the heights of the poles in image coordinates (you can write some code to automatically select points in the image, or you can hard-code these measurements). From these image measurements and the 3D quantities specified above, derive and compute an estimate for the camera focal length, and then the 3D height of the blue pole. Submit a document showing your work on deriving these estimates.
Part 2: Dolly Zoom: As shown here, a dolly zoom is an in-camera effect that appears to undermine normal visual perception and has been a popular effect in many movies. This effect is accomplished by simultaneously adjusting the camera focal length and the distance between the camera and object of interest. Specifically, the effect can be achieved by moving the camera toward the object while simultaneously reducing the camera focal length such that the object remains the same size in the image and the background appears to change in volume relative to the object.
We will provide you with most of the code for creating a simple 3D scene consisting of a red cube in a checkered room and for creating the dolly zoom effect. You should write the function get_projective_matrix(). See the inline comments for the expected input and output to this function. Your submission should consist of this function along with the code we provide (so we can run and test your code).